Introduction:
In the vast and unpredictable wilderness, injuries are an inevitable part of the journey. Whether you are an avid hiker, camper, or explorer, understanding how to manage wounds within the desolate tract efficiently is vital to your protection and the safety of those around you.
Section 1: Assessing the Situation
Before leaping into the first resource, it is important to evaluate the situation and ensure the safety of everyone. Evaluate ability dangers consisting of volatile terrain, flora and fauna, or destructive weather conditions. Once the scene is steady, proceed with the following steps:
Stay Calm: Panic can exacerbate the scenario. Take a deep breath, assess the system, and be composed.
Call for Help: If viable, use a verbal exchange tool to name expert clinical help. Provide accurate information approximately the vicinity, the nature of the damage, and the range of humans concerned.
Section 2: Basic First Aid for Minor Wounds
Minor wounds, cuts, scrapes, and blisters are not unusual inside the desert. Proper first resources can save you infections and similar headaches:
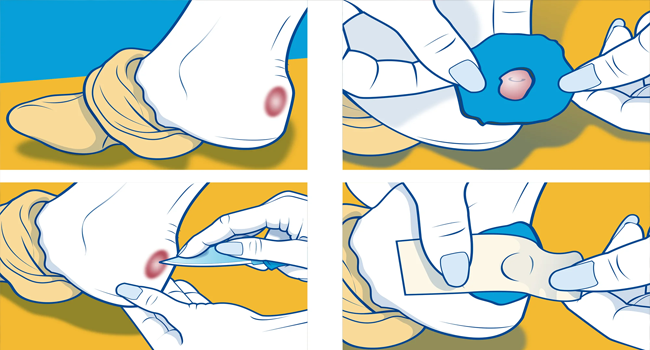
Clean the Wound: Use clean water or an antiseptic wipe to smooth the wound softly. Remove any debris, inclusive of dust or splinters.
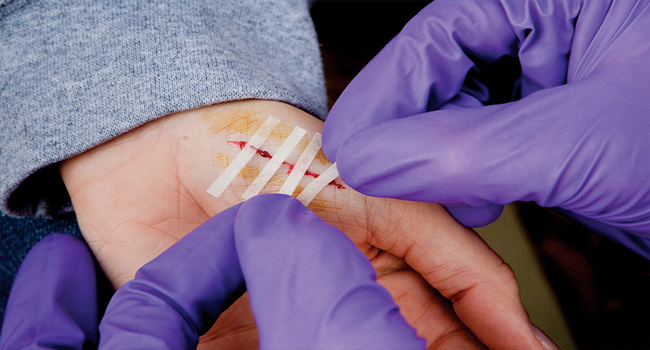
Apply an Antiseptic: Use an antiseptic ointment to save you from contamination. Carry a small, first useful resource package with bandages, gauze, and adhesive tape.
Elevate if Possible: If the injury is on an extremity, raise it to lessen swelling.
Section 3: Dealing with Major Wounds
In the case of extra intense wounds, along with deep cuts, puncture wounds, or fractures, additional steps are essential:
Stabilize Fractures: If a fracture is suspected, immobilize the injured place using splints or improvised substances like sticks and bandages.
Protect from Elements: Protect the injured individual from the elements with clothing or a makeshift shelter, if essential, to save you from hypothermia or overheating.
Section 4: Hydration and Nutrition
Proper hydration and nutrition are critical for the body’s herbal recovery procedure. Ensure the injured person stays hydrated and consumes a balanced diet if feasible. Dehydration can obstruct recovery, so inspire common sips of water.
Section five: Wilderness-Specific Considerations
The desert affords particular challenges that require specific concerns while coping with wounds:
Wildlife Concerns: Be privy to nearby wildlife and take precautions to avoid encounters. Treat animal bites or stings right away and seek scientific attention.
Waterborne Hazards: If the wound includes touch with water, consisting of a river or lake, thoroughly clean and disinfect the wound to prevent waterborne infections.
Section 6: Psychological Support
In addition to bodily care, emotional well-being is vital in a barren region emergency:
Provide Reassurance: Keep the injured person calm by offering reassurance and explaining the steps being taken for their care.
Monitor for Shock: Watch for signs of surprise, including faded pores and skin, speedy breathing, or confusion. Keep the character warm and comfortable.
Section 7: Evacuation and Communication
In many wasteland situations, the nice direction of motion is to evacuate the injured character to a scientific facility as quickly as feasible. Here are a few key points to take into account:
Create a Makeshift Stretcher: If the injured character is unable to stroll, improvise a stretcher with the usage of strong branches, garb, or other available substances. Ensure the individual is secure and comfortable in the course of shipping.
Coordinate with Emergency Services: Provide ordinary updates to emergency services concerning the injured character’s situation and vicinity. Follow their steering on the first-rate evacuation route.
Maintain Communication: If you have a communication tool, hold it charged and use it judiciously. Signaling gadgets, whistles, or signal mirrors may be useful in far-off regions.
Section 8: Continual Assessment and Adaptation
As time progresses, continually re-examine the injured individual’s situation. Wounds might also evolve, and shock or contamination symptoms can become extra apparent. Be organized to develop your first useful resource measures based on those observations.
Check Circulation: Ensure that blood circulation to extremities is not compromised. Adjust bandages or reposition the character if essential.
Monitor Vital Signs: If you’ve got the way, screen critical signs with a pulse, respiratory charge, and temperature. Report any sizable changes to clinical professionals.
Section 9: Preventative Measures
Preventing injuries is as important as treating them. Incorporate those preventative measures into your barren region excursions:
Proper Gear and Footwear: Wear appropriate garb and shoes to reduce the danger of cuts, blisters, and accidents. A properly organized adventurer is much less likely to come across extreme issues.
Navigation Skills: Improve your navigation talents to avoid getting misplaced, decreasing the chance of prolonged exposure to the elements.
Knowledge of Local Hazards: Research and understand the precise, demanding situations and hazards of the desolate tract you’re exploring. This know-how assists you in preparing for and mitigating dangers.
Section 10: Wilderness First Aid Training
One of the only methods for dealing with wounds within the desolate tract is to undergo the wasteland’s first useful resource education. These publications provide palms-on experience and in-depth knowledge of how to reply to various emergencies. Protected topics often include wound care, splinting, evacuation approaches, and environmental management. Consider enrolling in a reputable wasteland first resource course to decorate your skills and confidence in handling emergencies.
Section 11: Building a Comprehensive First Aid Kit
A nicely-ready first aid kit is crucial for any desolate tract day trip. Customize your package primarily based on the activities you’ll be undertaking and the dangers of the surroundings. Some objects to include are:
Bandages and Sterile Dressings: Various sizes for protecting wounds of different severities.
Antiseptic Wipes and Ointment: For cleaning and disinfecting wounds.
Adhesive Tape and Band-Aids: To stable dressings and cover minor cuts.
Scissors and Tweezers: Useful for slicing tape, doing away with splinters, or reducing garb to get right of entry to wounds.
Splints and Elastic Bandages: For stabilizing fractures and assisting injured limbs.
Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatories: Over-the-counter medicinal drugs can help control aches and reduce infection.
Emergency Blanket: Provides warmth in case of publicity to bloodless weather.
Communication Device: A charged cell phone, satellite smartphone, or two-way radio for calling for help.
Water Purification Tablets: In case easy water sources are scarce.
Whistle and Signal Mirror: For signaling in case of emergencies.
Multi-tool or Knife: Useful for numerous duties, reducing clothing or improvising splints.
Section 12: Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding the criminal and moral aspects of imparting the first resource in the wasteland is important. Good Samaritan laws might also defend you, but acting within your scope of education and competencies is important. Always prioritize your safety and the protection of others, and do not hesitate to seek expert medical assistance when needed.
Section 13: Team Dynamics and Leadership
In a group setting, powerful conversation and leadership are paramount. Designate roles and duties amongst team contributors to streamline the response to wasteland damage. Establishing clear communique channels guarantees that everyone is informed and may contribute to the quality of their skills. A chief should be peaceful, coordinate efforts, and make knowledgeable choices for the group’s well-being.
Section 14: Mental Preparedness
Wilderness accidents may be emotionally tough for each injured birthday celebration and those offering resources. Mental preparedness involves information on the capability of stressors and developing coping strategies. Encourage open communication inside the organization, fostering supportive surroundings. Recognize signs and symptoms of emotional misery and provide reassurance. Mental resilience is a valuable asset in handling wasteland emergencies.
Section 15: Environmental Considerations
The wasteland environment can pose additional challenges while coping with wounds. Consider elements together with severe temperatures, high altitudes, or dense vegetation. Adapt your first useful resource technique accordingly, considering the impact of the environment on the injured person’s circumstance. Protect against elements, maintain appropriate frame temperature, and take note of capacity environmental hazards throughout the response.
Section 16: Recording and Reporting
Documenting the details of the incident and the care furnished is vital for continuity of care and reporting to scientific specialists. Record the time of the damage, the character of the wound, the first resource measures taken, and any changes in the individual’s circumstance. These statistics may be valuable while seeking scientific help and can inform healthcare professionals about the damage’s extent.
Section 17: Continuous Learning and Improvement
As generation and scientific knowledge evolve, so must your desert first aid skills. Stay updated on the brand-new strategies and advancements in first aid. Attend refresher publications, take part in simulations, and examine actual-existence reviews. Continuous gaining knowledge enhances your ability to conform to new challenges and ensures that your abilities remain sharp for any future wasteland adventures.
Conclusion:
Effectively dealing with wounds in the wilderness requires a combination of preparedness, knowledge, and a calm demeanor. By expertise in fundamental first resource ideas, assessing the situation, and thinking about the precise challenges of the desolate tract, you may ensure a quality viable outcome for yourself and the people with you. Remember, at the same time as these pointers are useful, expert scientific assistance must be sought as quickly as feasible for greater intense injuries. Stay safe and experience the exquisite exterior responsibly!